Volatility as an indicator of uncertainty
Volatility represents the change in the value of a currency and is of interest to us to the extent that it affects the company’s international operations. It represents risk in the risk/return tradeoff. When we talk about volatility, we usually refer to the magnitude and frequency of market fluctuations.
For the company whose functional currency is the Canadian dollar (CAD), a CAD 1 million business transaction does not involve currency risk.
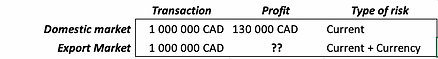
However, when it sells abroad, this currency risk is added to all the other risks, bore by the company on its domestic market.
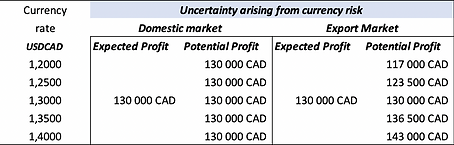
Foreign exchange risk management seeks to ensure that the risk-adjusted profitability obtained on the foreign transaction is at least comparable to the one on the domestic market.
Currency volatility becomes a key element in comparing the anticipated profitability of commercial transactions in different markets.
Factors influencing currency volatility
Several factors impact the volatility of the foreign exchange market. [1]Monetary policy has a direct impact on currency flows. Central banks through their policies use interest rates to control the money supply in circulation. The importance of monitoring the decisions of central banks such as the US Federal Reserve, the European Central Bank (ECB) and other institutions such as the monetary authorities of Canada and Japan is well established.
Trade wars are frequent and generate a lot of volatility. Whether we think of the one between China and the US, between the UK and Europe, or even the one between Canada and the US, these trade wars cause disruptions on the currencies involved because billions of transactions are affected. Questions of ” geopolitics ” also play a role.
Whether it is public health decisions (the purchase of vaccines against the Coronavirus in large quantities), or the military tensions between Ukraine and Russia, policies decided by our governments have a permanent impact on the currencies to which they are attached.
In this sense, it is important not to underestimate what the perception of events by currency traders can do to the volatility of a currency pair and, above all, how it can quickly change the market landscape. In fact, this market sentiment is reflected in the implied volatility used to price an option[2]. When markets exchange rates are complacent, implied volatility is relatively low, but implied volatility increases when fears and uncertainty arise from an unstable environment.
Originally, however, it must be remembered that volatility is a direct function of liquidity. Liquidity can be defined as the amount of supply and demand in the market and the greater these are, the more difficult it is for market participants to have an impact on prices. So, the higher the liquidity is, the lower is the volatility, and vice versa.
Impact on SMEs
Volatility impacts SMEs operating internationally in different ways. Large market fluctuations generate greater uncertainty about flows. Making sure you have the right amount in the right currency at the right time to cover payments from customers and suppliers becomes perilous. The cash position is more uncertain. [3]
The higher the volatility, the larger the size of trading transactions will have to be taken into account as a critical tolerance threshold can be exceeded more quickly. The same will apply to points of purchase and sale in cash or forward; fragmenting its interventions in the market over a longer period of time and several times takes its full importance.
The currency pairs that the SME trades are determined by its choice of suppliers (imports) and the markets it chooses to develop internationally (exports).

Therefore, estimating the competitive advantage of a foreign supplier, for example, must, among other things, take into account the volatility of the currency pair and the costs of managing the risks involved.
Ultimately, it is the profitability of the company that is affected.
Estimating volatility
It is possible to calculate historical volatility for a given currency pair to get an indication of its risk. In this case, it is the calculation of the standard deviation of rate movements for a period in the past. The standard deviation is a measure of the dispersion of possible values around their average.
The price of a currency pair regularly deviates from its average value, which significantly depends on the geopolitical context of the moment. In this case, it becomes difficult to use the average as a reference because there is a high probability of extreme price movements, both in amplitude and in terms of direction.
The level of volatility also affects the price of options. In fact, the price of the latter reflects an anticipated level of volatility. In this case, we are talking about implied volatility. It should be noted that volatility tends to change over time and is therefore not constant.
Since not all currencies are equal in the foreign exchange market, some have higher impact volatility than others. Therefore, the impact on the profitability of the company will not be the same depending on the currencies in which the transactions are denominated.
We will discuss in a future article the inclusion of these different impacts in the budget process.
[1] Read more: it’s not just the economy that’s growing, uncertainty too…
[2] It will be discussed further later
[3] Read more: Foreign exchange risk: defining a cash flow
[4] Read more: The extent of foreign exchange risk
__________________________________________________________
International markets: a world of opportunities
Expanding business abroad is a source of growth, but it also entails risks for SMEs. It is also complex to monitor the successive impacts of exchange rates on the company’s anticipated performance.
D-Risk FX Budget & BI, offers SMEs performance, risk and test scenario analyses, broken down by market, currency and business line, with a tailor-made hedging strategy and real-time monitoring of the company’s anticipated performance.
Gain autonomy, automate your processes and approach your foreign markets with the security of a clear foreign exchange risk management strategy and monitoring that matches your ambitions.



